Unit 30: Page Layout Design
Introduction
Introduction
Introduction to BTEC DCP Unit 30
The in-class teaching of these topics will provide you with the knowledge to complete the assignment. The assignment will be due on completion of the module. The deadline is confirmed within the Assignment Brief.
Contact information
Mr Goulding is available at bg@range.sefton.sch.uk. Replies will be prompt during school hours. Outside of school hours, responses may be delayed.
Assignment 1 Content
Print Design Considerations
Print Design Considerations
Print Design Considerations
Why do some people prefer printed products?
Many products are becoming digital. Yet some people still prefer to use paper-based products. For example:
- Newspapers
- Posters
- Adverts
- Packaging
- Business cards
Some people prefer the tactile, tangible and physical feeling of paper which digital products do not provide. You cannot 'feel' a website in your hands in the same way that you can hold a newspaper. Some people prefer the tactile nature of physical products. In a way, some believe that printed products are more 'fun' and 'relaxing' to use than digital products.
Some people also find printed products safer and more reassuring. It is easy to lose digital data when a device becomes faulty. Some people believe that it is safer to store printed products inside their physical filing cabinet. This may reduce anxieties surroudning data loss, identity theft or the loss of a mobile digital device.
Some users find paper easier to read from in comparison to digital products. Some also believe that reading from a static piece of paper is less distracting for them in comparison to a digital product which is live and may have irritating popups or other distractions. This is another reason why some prefer to use paper-based products.
You can read more about this here.
Benefits and drawbacks of print design
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Print documents are physical which provide a tactile and/or textured experience. Some people prefer this experience. | When printing products onto paper, there is a risk of print errors. |
| Print design is consistent. The experience is the same for every person who sees it. | Printed products are static. This makes it difficult for changes to be made. Once a product has been shipped, it would need to be re-printed for changes to be made. |
| Print design makes possible special effects. For example, letterpress and embossing. This can enhance the tactile experience which some people prefer. | It can be expensive and time consuming to print products. |
| Print design uses RGB (red, green and blue) colours. This is also known as CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black). This provides for 16,777,216 colours. This allows us to be incredibly precise with colours. | Interactivity of printed products is highly limited when compared to digital products. You can't have animations or buttons with paper. Interaction is limited to turning a physical page. |
| Printed products allow us to use a high amount of dots per inch (DPI). This is the print equivalent of a high resolution (pixels per inch or PPI). | |
| Printed products can be highly effective for marketing purposes. |
Letterpress and embossing
Letterpress and embossing are examples of special effects that can be applied to printed products. A letterpress creates an "impression" on a piece of paper. Both techniques are intended to enhance the appearance and tactile nature of the product:

Embossing is a technique that raises part of a printed product. This effect can be found on business cards and debit cards:

Page elements
This diagram shows the various elements of a printed product:

Digital Design Considerations
Digital Design Considerations
Digital Design Considerations
Pixels per inch (PPI)
This is a measure of how many individual square pixels per inch of a digital image (PPI). PPI is used to measure the resolution of a digital product. Whereas DPI (dots per inch) is used to measure the quality of printed products.
CMYK / RGB
CMYK (Cyan Magenta Yellow Key) refers to the four ink palates used for selecting colours. RGB (Red Green Blue) is a system used for choosing colours made by mixing red, green and blue. With RGB, there are 16,777,216 different possible colour combinations. The more colours we use, the more impressive and detailed an image will appear.
CMYK and RGB are important to consider because, the more colours we use, the more storage space an image will take up on the computer. This can be a problem for images uploaded to the internet. Every time a user visits a webpage, the user's computer downloads a copy of that website. If there are large image files on a website caused by using lots of different but similiar shades of the same colour, this will dramatically increase the file size of the website which can possibly cause the website to run slowly. This is because the user's computer will take longer to download that webpage because of the larger file size. This will give the appearance that the website itself is slow. This could also be a problem for people with limited mobile data plans. Larger image sizes will cause more data to be used when downloading the website file.
This must be carefully balanced with reducing the number of colours used. If we don't use enough colours, an image may not look right. The image may appear to be poor quality. This will affect the user's experience. This is not a problem for printed products, we can use as many colours as we like. This is because the user doesn't need to download the file. It is a static printed product.
Responsive page design
It is important for websites to be designed to work on all devices. For example:
- Desktop computers / laptops
- Tablets such as iPads
- Mobile phones
This is important to consider because each of these devices has a different sized screen. This means that each device will need to display a website in a different way for the user to have a good experience. For example, the full desktop version of a website would not be suitable for a mobile device. For this version to fit on the screen, the buttons and text would need to be very small. This would make it difficult to use the website without zooming in. This is not a positive user experience.
We can resolve these problems by using responsive page design. This involves changing the layout of a website based on the size of the user's screen. I have used responsive design with this website. There is a different layout for desktop screens and mobiles:
Space available
With digital products, are not limited by space like with printed products. A website can be as big as we like. Whereas physical products must be printed at cost and stored somewhere. This means that we are limited on space with physical products.
For example, a newspaper only has a certain amount of physical space. Whereas an online news site can have as many articles as the publisher wishes. Physical space is not restricted. The only consideration would be file size for the same reasons given above.
Interactivity
Digital products can be highly interactive. We can have buttons, animations, games and more. This interactivity is not possible to the same extent with static physical products which have been printed.
Dynamic content
Digital products allow content to be dynamic rather than static such as with printed products. If we notice a typo on a website, we can amend the website without cost. If a typo was noticed on a newspaper, the cost of amending this error could be prohibitive if the newspaper has already been sent to print. It would not be practice to make such changes.
Navigation
With digital products, Navigation is a way of moving around a digital product with buttons. For example, on a website, we often have a navigation bar with buttons that allows the user to move between pages on the website.
With this website, there are navigation buttons that allow the user to move between topics:
Transitions / effects
Digital products can have special effects such as animations and fade in/out transitions. These are possible because digital products can be dynamic rather than static. Text printed on a page cannot have transitions or effects applied in the same way as digital products.
Page Elements Explained

Evaluating Products
Evaluating Products
Evaluating Products
For your assignment, you will need to choose two printed and digital products (four in total) to evaluate. These must be high quality to achieve distinction criteria.
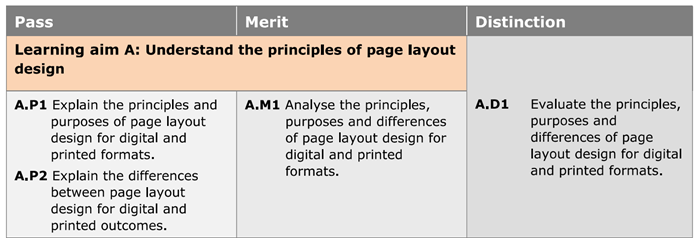
In your assignment, you must explain the principles of page layout design used, analyse the products, and evaluate them. To secure a distinction grade, you must satisfy ALL of the pass, merit and distinction criteria shown below. For example, if you miss one criteria in the 'Distinction' column, you will be confined to a maximum of a merit. If you miss a criteria in the 'Merit' column, you will be confined to a pass grade. If you miss a criteria in the 'Pass' column, you will be unsuccessful at the assignment.
Downloads
Assignment 1
Assignment 1
Introduction to Assignment 1
The first assignment will cover the principles of page layout design. In this assignment, you will be expected to produce a report on the principles of page layout design, comparing how digital and printed page layouts use common design principles for a specific audience and purpose.
The assignment will be assessed based on the following criteria:
